SEPlendid Developer Guide
1. About SEPlendid
SEPlendid is a Course Mapping System that allows NUS Computing students to seamlessly plan for their overseas courses, for the highly coveted Student Exchange Programmes (SEP). As a student, you can view and find course mappings in order to plan for your overseas studies without the hassle of creating complex Excel sheets. Utilise SEPlendid's course mapping function in order to quickly find possible mappings for certain courses you want to map. Finally, SEPlendid's note-taking system will assist you in organising your important information you will need for planning for your courses.
2. Table of Contents
- About SEPlendid
- Table of Contents
- Setting up, Getting Started
- Design
- 4.1 Architecture
- 4.2 UI Component
- 4.3 SEPlendidLogic Component
- 4.4 Model Component
- 4.5 Storage Component
- 4.6 Common Classes
- Implementation
- 5.1 Parser to Handle Commands with Optional Arguments
- 5.2 List Feature
- 5.3 Add Feature
- 5.4 Delete Feature
- 5.5 Update Feature
- 5.6 Search Feature
- 5.7 Sort Feature
- 5.8 Mapping Feature
- Other Helpful Guides
- Requirements
- 7.1 Product Scope
- 7.2 User Stories
- 7.3 Use Cases
- 7.4 Non-Functional Requirements
- 7.5 Glossary
- Instructions for Manual Testing
- 8.1 Launch and Shutdown
- 8.2 Local Course
- 8.3 Partner Course
- 8.4 University
- 8.5 Mapping
- 8.6 Note
- 8.7 Saving Data
- Planned Enhancements
- Effort
- Acknowledgements
3. Setting up, Getting Started
Refer to the guide Setting up and getting started.
4. Design
This section highlight the design considerations for SEPlendid.
4.1 Architecture
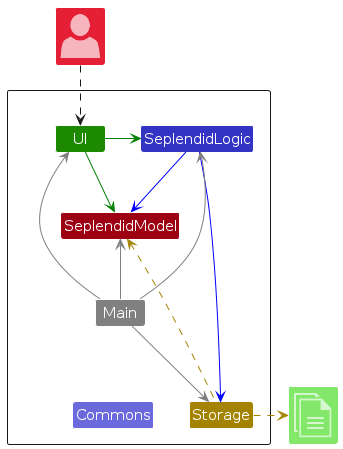
The Architecture Diagram given above explains the high-level design of the App.
Given below is a quick overview of main components and how they interact with each other.
Main components of the architecture
Main (consisting of classes Main and MainApp) is in charge of the app launch and shut down.
- At app launch, it initializes the other components in the correct sequence, and connects them up with each other.
- At shut down, it shuts down the other components and invokes cleanup methods where necessary.
The bulk of the app's work is done by the following four components:
UI: The UI of the App.SeplendidLogic: The command executor.SeplendidModel: Holds the data of the App in memory.Storage: Reads data from, and writes data to, the hard disk.
Commons represents a collection of classes used by multiple other components.
How the architecture components interact with each other
The Sequence Diagram below shows how the components interact with each other for the scenario where the user issues the command note delete [1].
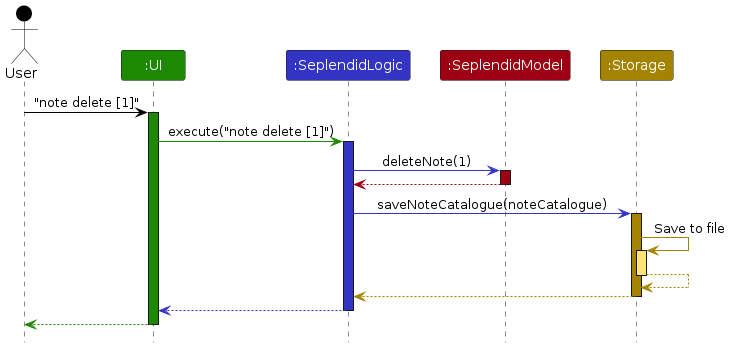
Each of the four main components (also shown in the diagram above),
- defines its API in an
interfacewith the same name as the Component. - implements its functionality using a concrete
{Component Name}Managerclass (which follows the corresponding APIinterfacementioned in the previous point.
For example, the SeplendidLogic component defines its API in the SeplendidLogic.java interface and implements its functionality using the SeplendidLogicManager.java class which follows the SeplendidLogic interface. Other components interact with a given component through its interface rather than the concrete class (reason: to prevent outside component's being coupled to the implementation of a component), as illustrated in the (partial) class diagram below.
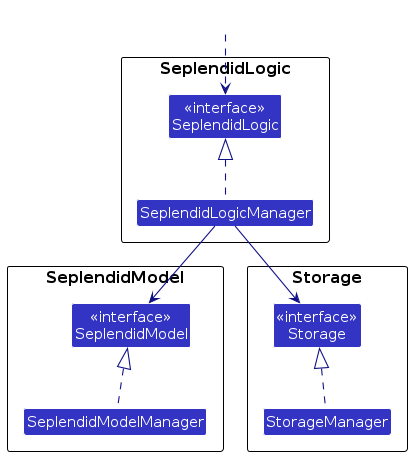
The sections below give more details of each component.
4.2 UI Component
API : Ui.java
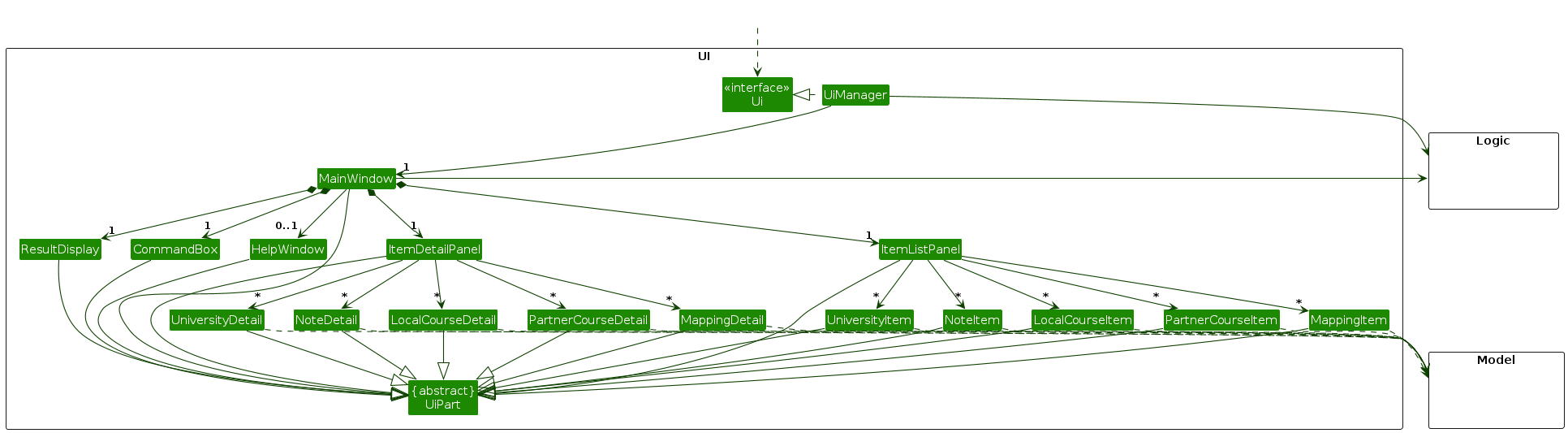
The UI consists of a MainWindow that is made up of parts e.g.CommandBox, ResultDisplay, ItemListPanel, ItemDetailPanel etc. All these, including the MainWindow, inherit from the abstract UiPart class which captures the commonalities between classes that represent parts of the visible GUI.
The UI component uses the JavaFx UI framework. The layout of these UI parts are defined in matching .fxml files that are in the src/main/resources/view folder. For example, the layout of the MainWindow is specified in MainWindow.fxml
The UI component,
- executes user commands using the
SeplendidLogiccomponent. - listens for changes to
Modeldata so that the UI can be updated with the modified data. - keeps a reference to the
SeplendidLogiccomponent, because theUIrelies on theSeplendidLogicto execute commands. - depends on some classes in the
Modelcomponent, as it displaysLocalCourse,PartnerCourse,University,Mapping, andNoteobjects residing in theModel.
4.3 SeplendidLogic Component
API : SeplendidLogic.java
Here's a (partial) class diagram of the SeplendidLogic component:

The sequence diagram below illustrates the interactions within the SeplendidLogic component, taking execute("note delete [1]") API call as an example.
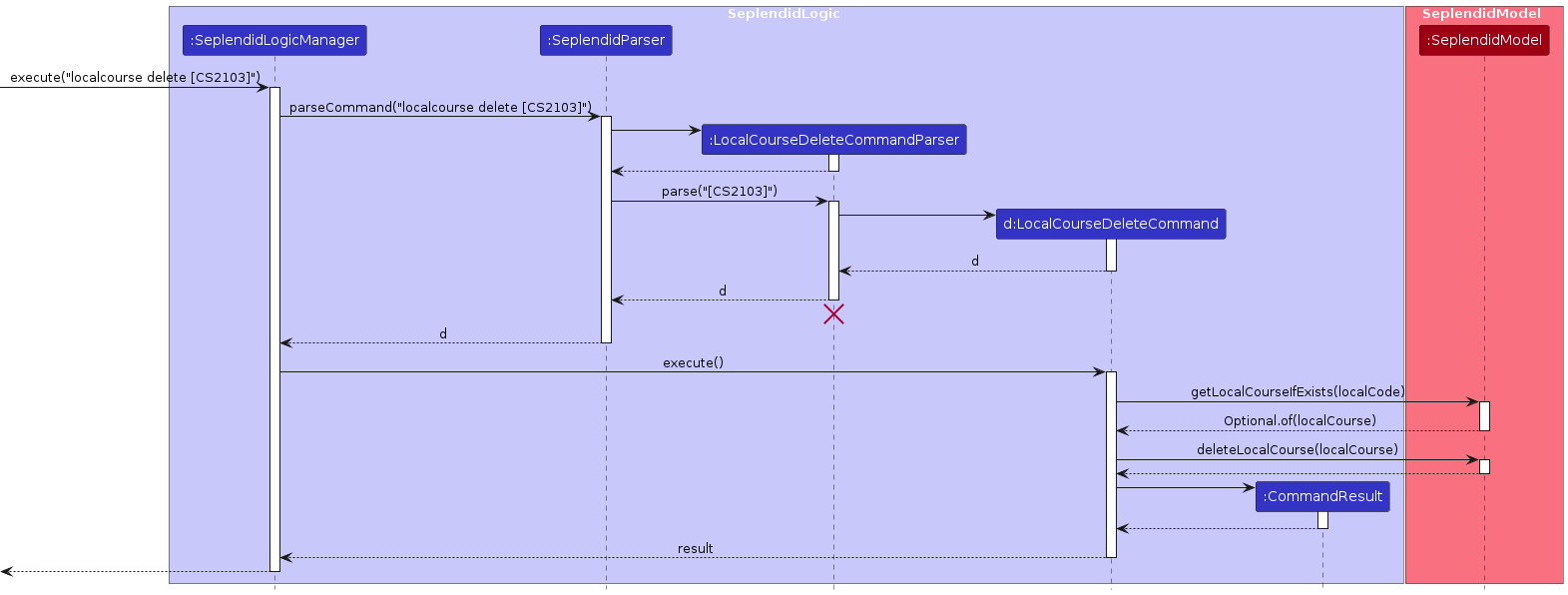
Note: The lifeline for NoteDeleteCommandParser should end at the destroy marker (X) but due to a limitation of PlantUML, the lifeline reaches the end of diagram.
How the SeplendidLogic component works:
- When
SeplendidLogicis called upon to execute a command, it is passed to anSeplendidParserobject which in turn creates a parser that matches the command (e.g.,NoteDeleteCommandParser) and uses it to parse the command. - This results in a
Commandobject (more precisely, an object of one of its subclasses e.g.,NoteDeleteCommand) which is executed by theSeplendidLogicManager. - The command can communicate with the
SeplendidModelwhen it is executed (e.g. to delete a note). - The result of the command execution is encapsulated as a
CommandResultobject which is returned back fromSeplendidLogic.
Here are the other classes in SeplendidLogic (omitted from the class diagram above) that are used for parsing a user command:
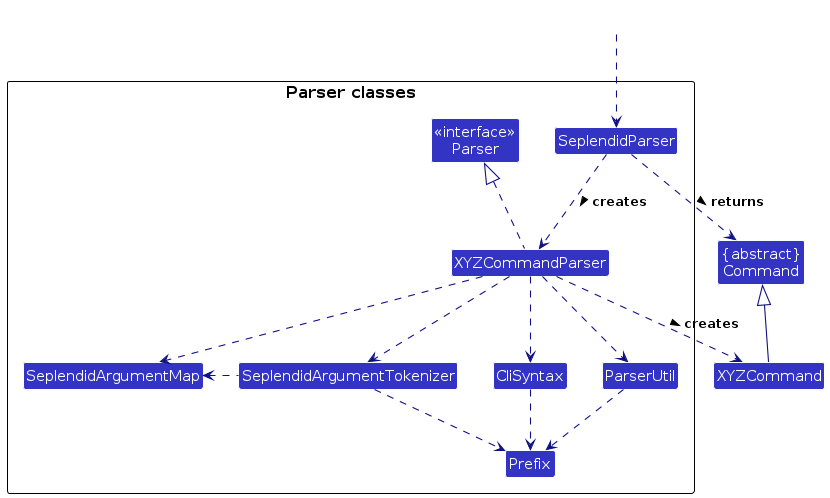
How the parsing works:
- When called upon to parse a user command, the
SeplendidParserclass creates anXYZCommandParser(XYZis a placeholder for the specific command name e.g.,LocalCourseAddCommandParser) which uses the other classes shown above to parse the user command and create aXYZCommandobject (e.g.,LocalCourseAddCommand) which theSeplendidParserreturns back as aCommandobject. - All
XYZCommandParserclasses (e.g.,LocalCourseAddCommandParser,NoteDeleteCommandParser, ...) inherit from theParserinterface so that they can be treated similarly where possible e.g, during testing.
4.4 Model Component
API : SeplendidModel.java
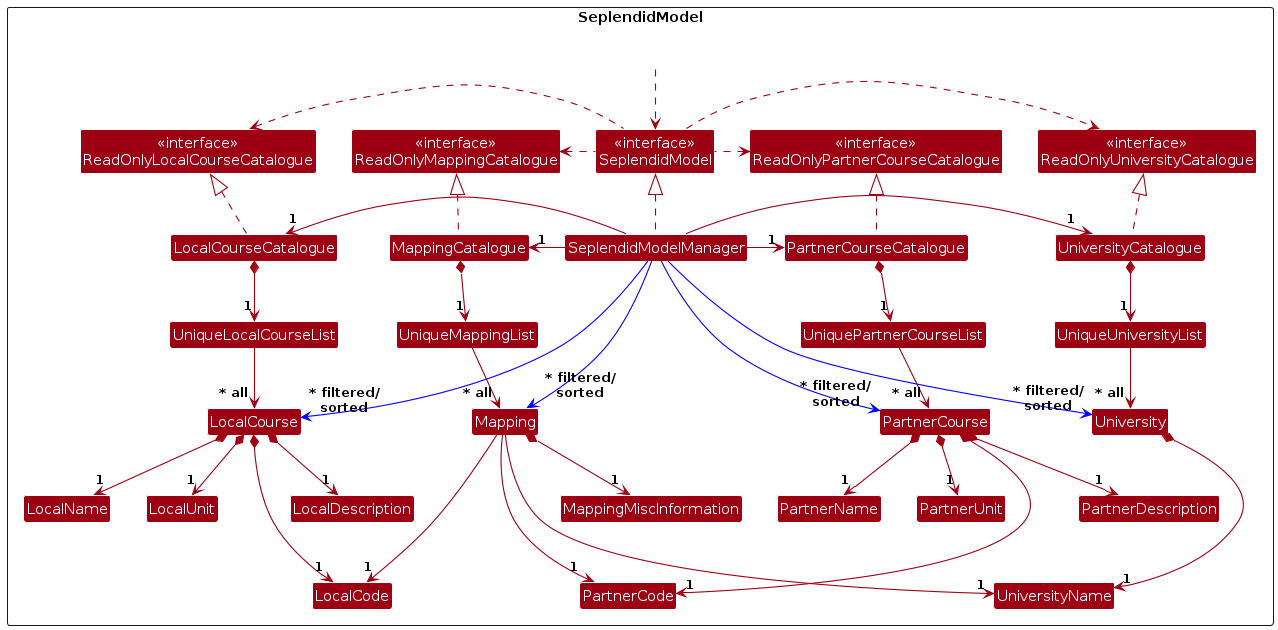
The SeplendidModel component,
- stores the local course, partner course, university, mapping and note data.
SeplendidModelManageralso serves as the facade class, for other components to access the data. It stores all the data, which the UI can access to display. Commands also take in theSeplendidModelobject to perform their operations on the data. - stores the currently 'searched for'
LocalCourse,PartnerCourse,University,Mappingobjects as separate filtered lists, exposed to outsiders as unmodifiableObservableList<LocalCourse>,ObservableList<PartnerCourse>,ObservableList<University>andObservableList<Mapping>objects respectively (e.g. the UI can be bound to one of these lists so that the UI automatically updates when the data in the list changes). - does not depend on any of the other three components (as the
SeplendidModelrepresents data entities of the domain, they should make sense on their own without depending on other components) - Local course are represented by
LocalCourseobjects, which are stored in aUniqueLocalCourseListobject. EachLocalCoursehasLocalCode,LocalName,LocalDescriptionandLocalUnitobjects.PartnerCoursefollows similarly, andMappingdepends onLocalCode,PartnerCodeandUniversityNameobjects (on top of its ownMappingMiscInformation). - Information on
Notemodel components are omitted in the above diagram for brevity.
4.5 Storage Component
API : Storage.java
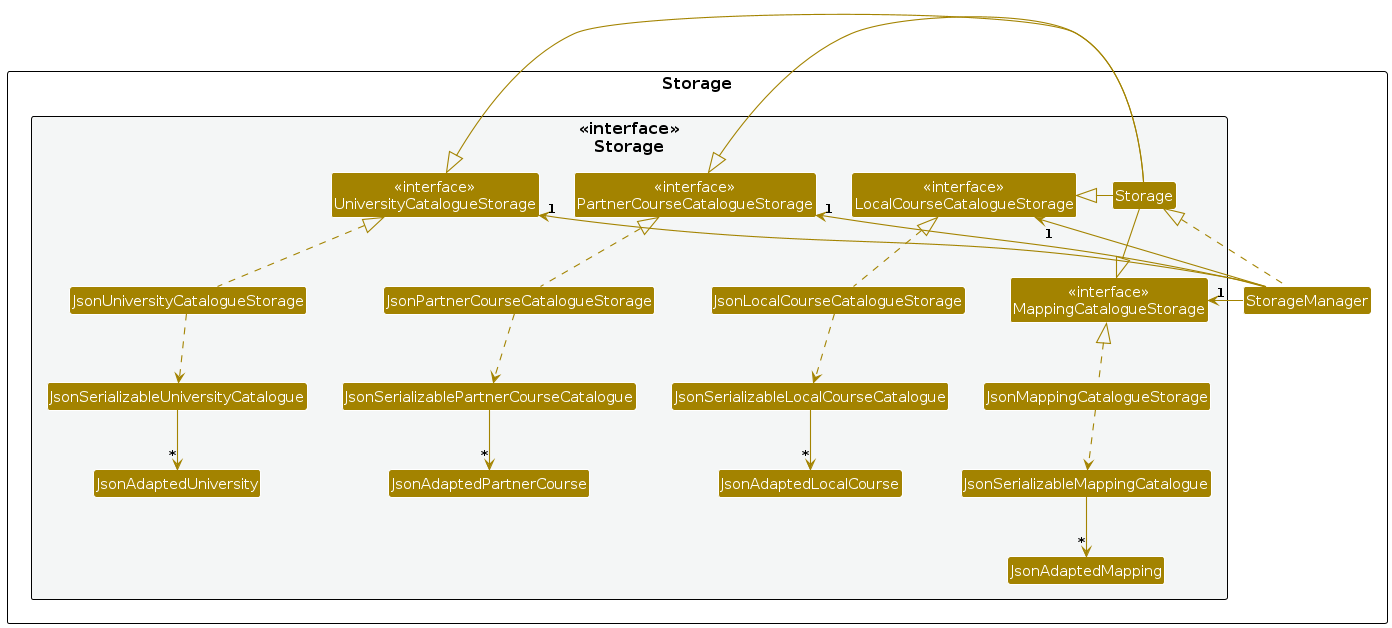
The Storage component,
- can save local course, partner course, university, mapping, note data and user preference data in JSON format, and read them back into corresponding objects.
- inherits from both
LocalCourseStorage,PartnerCourseCatalogueStorage,UniversityCatalogueStorage,MappingCatalogueStorage,NoteCatalogueStorageandUserPrefStorage, which means it can be treated as either one (if only the functionality of only one is needed). - depends on some classes in the
SeplendidModelcomponent (because theStoragecomponent's job is to save/retrieve objects that belong to theSeplendidModel). NoteCatalogueStorageandUserPrefStorageare omitted from the above diagram for brevity.
4.6 Common Classes
Classes used by multiple components are in the seedu.addressbook.commons package.
5. Implementation
This section describes some noteworthy details on how certain features are implemented.
5.1 Parser to Handle Commands with Optional Arguments
The below diagram gives a high-level overview on how the SeplendidParser parses a command from our command set:
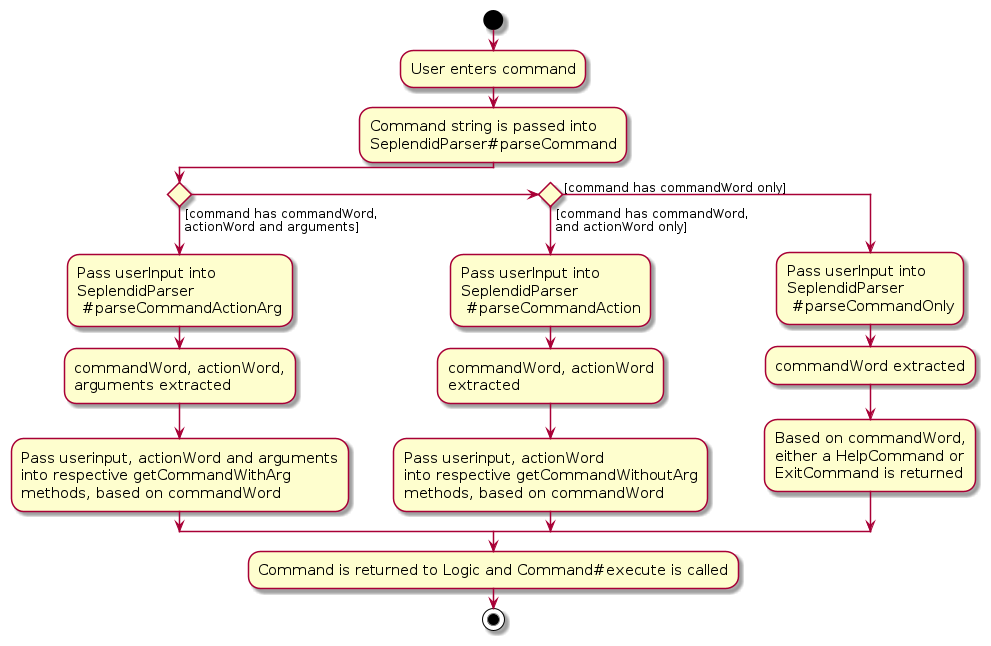
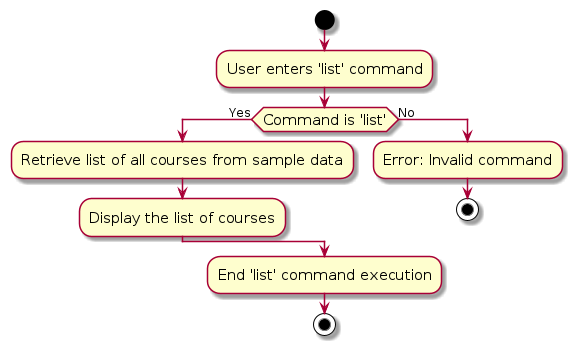
5.2 List Feature
Overview
The `list` command generates a list of SEPlendid data. The data can be in the for of a `localcourse`, `partnercourse`, `university`, `mapping`, or `note`. This allows the viewing of all the data type that is listed.
The activity diagram is as such:
Here is a sequence diagram for localcourse list:
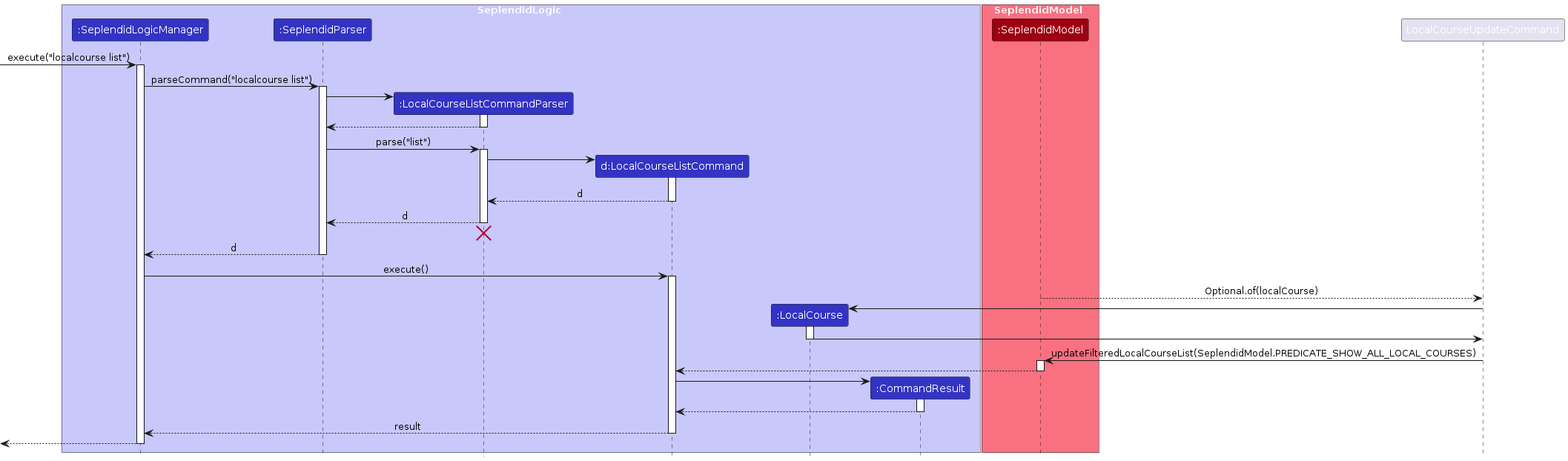
Feature Details
- The user specifies a data object with its required command word.
- If invalid command arguments are provided, the user will be prompted to enter the command correctly via an error message.
- If all the above steps are completed without exceptions, then the sample data of the specific data type will be displayed.
Feature Considerations
Each data type has to be specified to ensure organisation of sample data.
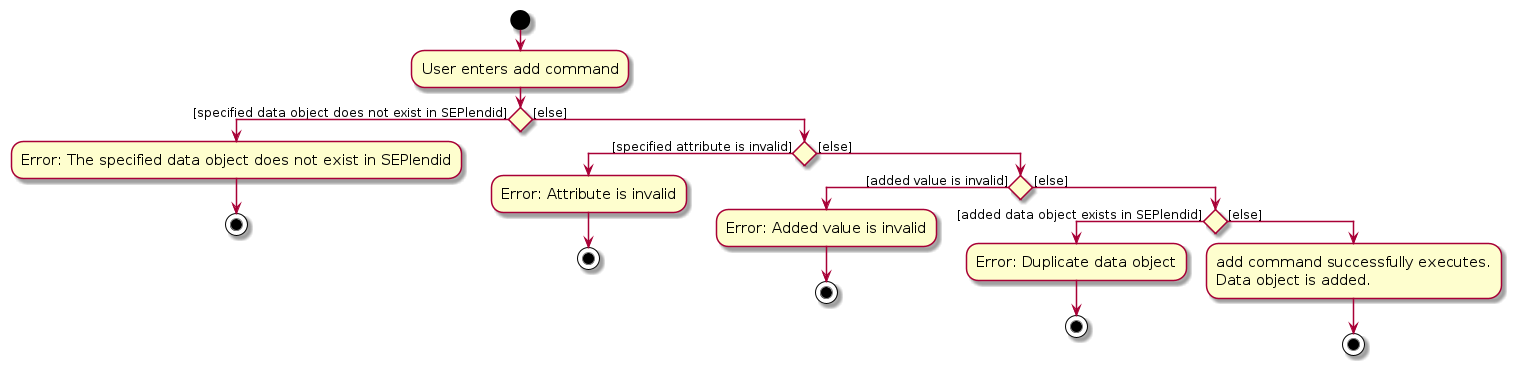
5.3 Add Feature
Overview
The add command allows for the adding of new courses, universities and notes. This allows the creation of new
datatypes.
5.3 Add Feature
Overview
The `add` command allows for the adding of `localcourse`, `partnercourse`, `mapping` and `notes`. This allows the addition of new data into SEPlendid.
The activity diagram is as such:
Here is a sequence diagram for note add:
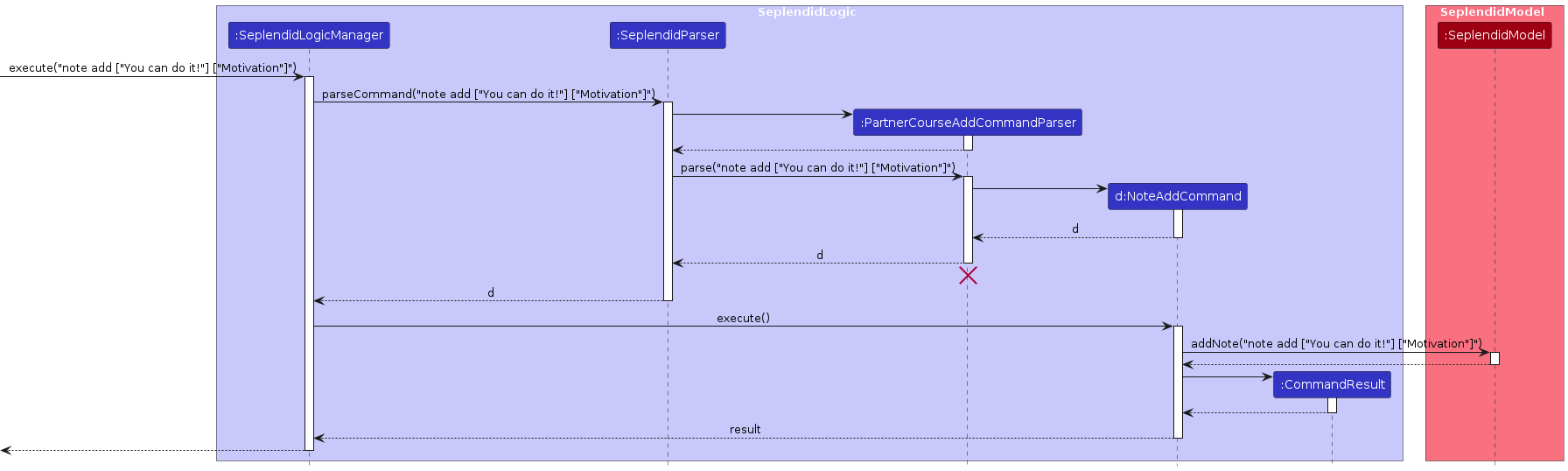
Here is a sequence diagram for partnercourse add:
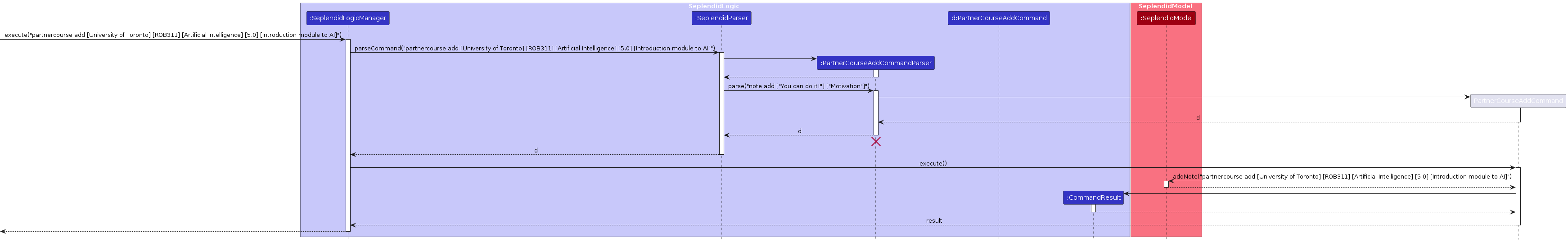
Feature Details
- The user is required to fill up all the attributes require to add the data object.
- If not all the identity attributes are provided, the user will be prompted to enter the command correctly via an error message.
- If the attribute is not applicable for
add, the user will be prompted to enter the attribute correctly via an error message. - If there exist the same identifying attributes, SEPlendid will raise an error message to the user.
- If all the above steps are completed without exceptions, then the data object is successfully queried.
Feature Considerations
It should be noted that when checking for duplicates in the UniqueLocalCourseList and UniquePartnerCourseList inside
SEPlendidModel, localcourse cannot have the same localcode and partnercourse cannot have the same partnercode
and universityname. This is because courses have unique course codes and is specific to the university, having this
check would also prevent confusion for users if they have mistakenly added courses that are already in the database.
Furthermore, this would confuse the user on which is the most accurate information available as well.
5.4 Delete Feature
Overview
The delete command deletes specified data object in SEPlendid, specified by their unique identity attributes.
Here is an activity diagram for delete localcourse:
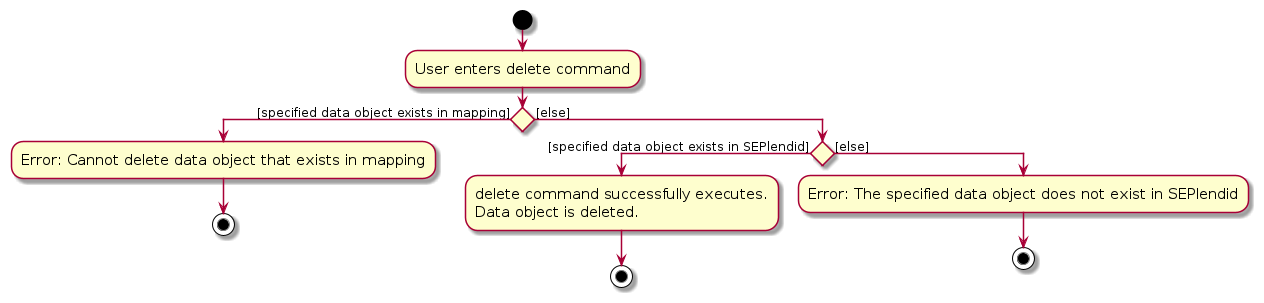
Here is a sequence diagram for delete:

Feature Details
- The user specifies a data object with its unique identity attribute(s).
- If the data object is non-existent, the user will be prompted to enter the identity attributes correctly via an error message.
- If not all the identity attributes are provided, the user will be prompted to enter the command correctly via an error message.
- If all the above steps complete without any exceptions, then the data object is successfully deleted.
Feature Considerations
The data object is only deleted when all the specified identity attributes are identical to an existing data object.
5.5 Update Feature
Overview
The update command updates specified attribute of a data object with updated value.
Here is an activity diagram for update localcourse:
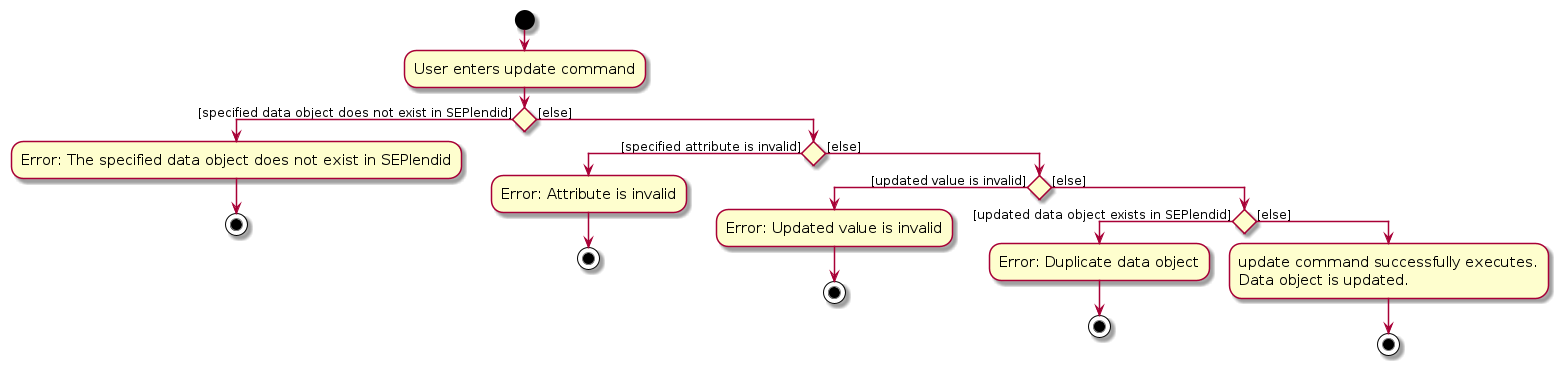
Here is a sequence diagram for update:
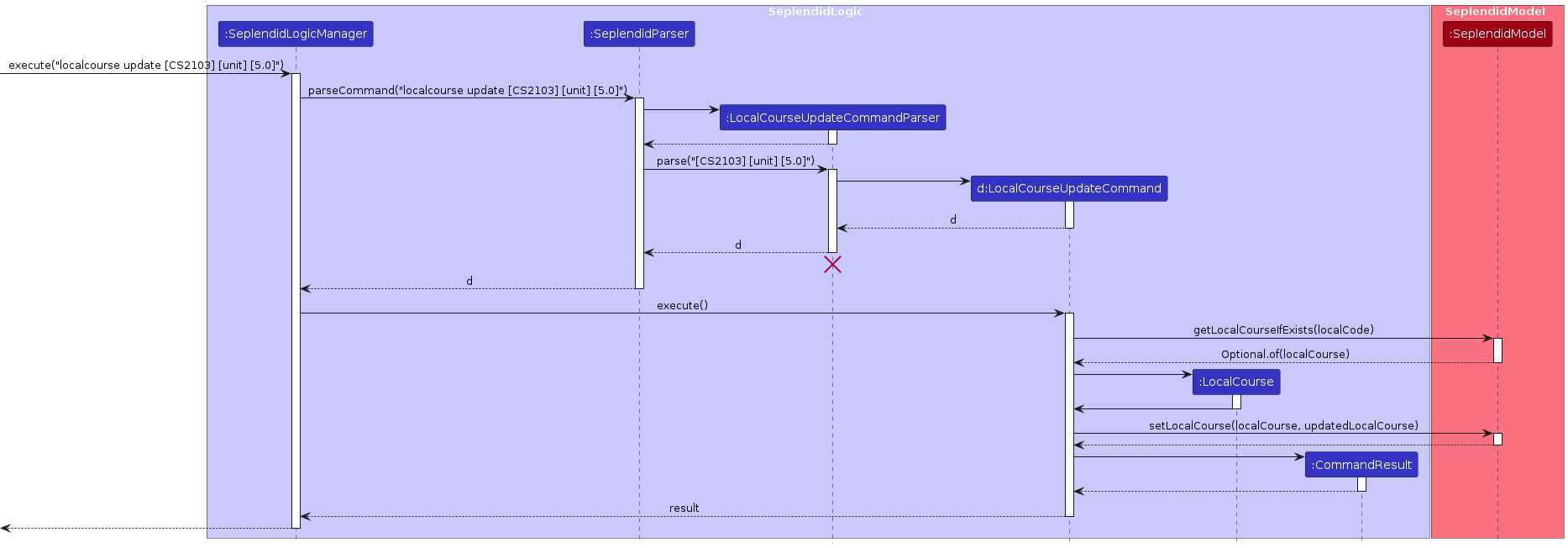
Feature Details
- The user specifies a data object with its unique identity attribute, attribute to be updated, and new value.
- If the data object is non-existent, the user will be prompted to enter the identity attributes correctly via an error message.
- If not all the identity attributes are provided, the user will be prompted to enter the command correctly via an error message.
- If the attribute is not applicable for
update, the user will be prompted to enter the attribute correctly via an error message. - If the updated data object exists in SEPlendid, an error is raised to inform the user.
- If all the above steps complete without any exceptions, then the data object is successfully updated.
Feature Considerations
The data object is only updated when all the specified identity attributes are identical to an existing data object. Each data type has different attributes that can be used for updating.
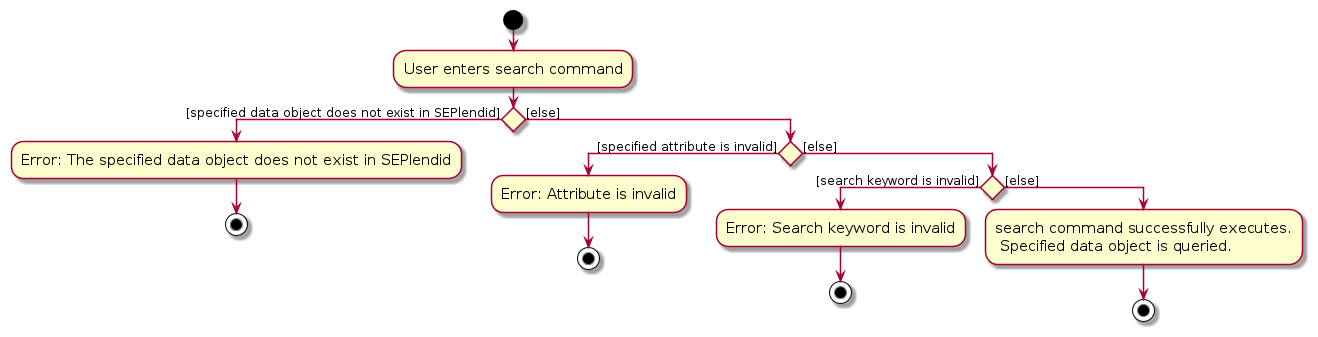
5.6 Search Feature
Overview
The search command allows users find specific courses or universities they are interested in. This allows for faster
querying of courses, universities and notes.
The activity diagram is as such:
Here is a sequence diagram for partnercourse search:
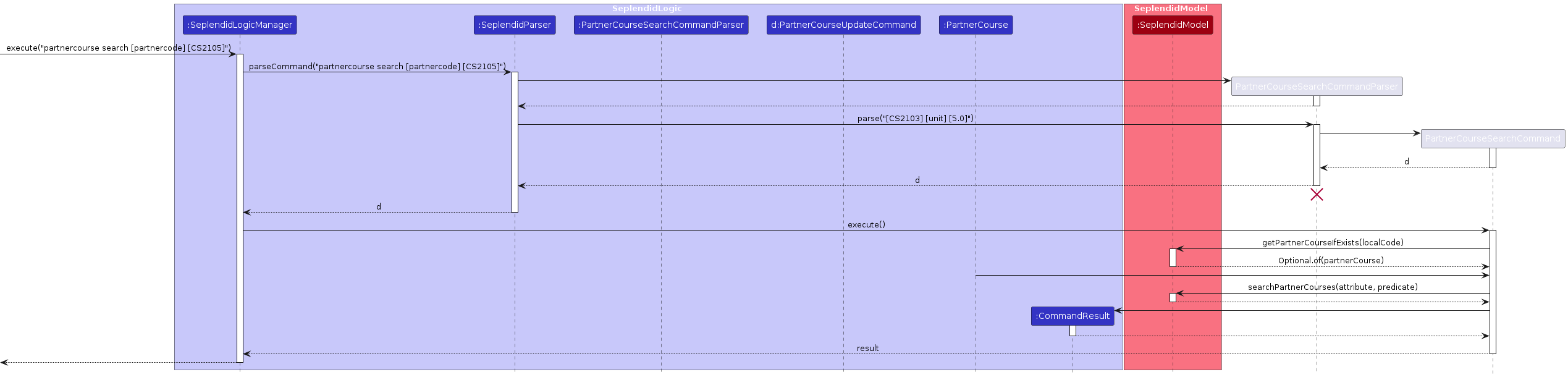
Feature Details
- The user specifies a data object with its unique identity attribute, attribute that they are querying and the keyword for the query.
- If the data object is non-existent, the user will be prompted to enter the identity attributes correctly via an error message.
- If not all the identity attributes are provided, the user will be prompted to enter the command correctly via an error message.
- If the attribute is not applicable for
search, the user will be prompted to enter the attribute correctly via an error message. - If all the above steps are completed without exceptions, then the data object is successfully queried.
Feature Considerations
The data object is only searched when all the specified identity attributes are identical to the existing data object. Each data type has different attributes that can be used for searching.
5.7 Sort Feature
Overview
The sort command sorts specified data objects by specified attributes.
Here is an activity diagram for sort localcourse:
Here is an sequence diagram for sort:
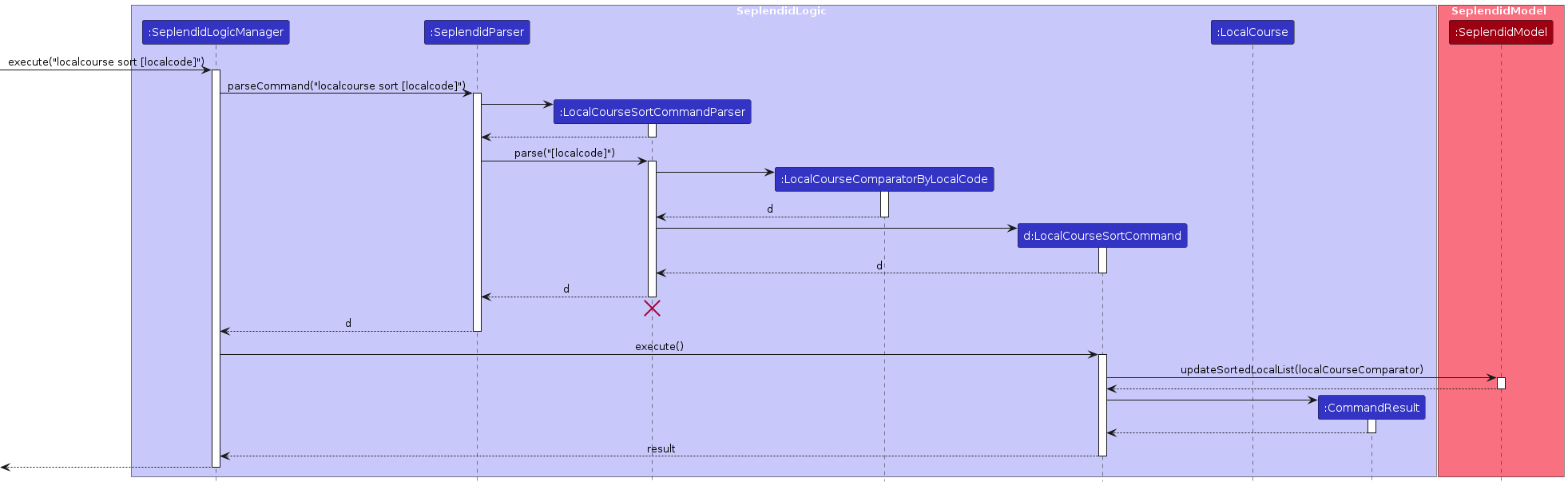
Feature Details
- The user specifies a data object and its attribute to sort.
- If the attribute is not applicable for
sort, the user will be prompted to enter the attribute correctly via an error message. - If all the above steps complete without any exceptions, then the data objects will be sorted by specified attribute.
Feature Considerations
Each data type has different attributes that can be used for sorting.
5.8 Mapping Feature
The mapping list/add/delete mechanism is facilitated by MappingCatalogue. It stores Mapping objects which
contain the LocalCode, UniversityName, PartnerCode and MappingMiscInformation objects. This means that
Mapping is dependent on LocalCourse, University and PartnerCourse classes (and their respective
LocalCourseCatalogue, UniversityCatalogue and PartnerCourseCatalogue).
A UniqueMappingList is stored internally in MappingCatalogue, ensuring that Additionally, it implements the
following operations (this list is not exhaustive):
MappingCatalogue#addMapping(Mapping)— Adds a mapping to the mapping catalogue, and throws aDuplicateMappingExceptionif the mapping already exists based on the primary key (LocalCode,UniversityName,PartnerCode).MappingCatalogue#removeMapping(Mapping)— Removes a mapping from the mapping catalogue, and throws aMappingNotFoundExceptionif the mapping does not exist.MappingCatalogue#hasMapping(Mapping)— Checks whether a mapping exists in the mapping catalogue, to use to- prevent duplicate insertion.
MappingCatalogue#hasMappingWithLocalCode(LocalCode)— Checks whether a mapping with the specifiedLocalCodeexists in the mapping catalogue, to use to prevent deleting aLocalCoursewith such aLocalCode.MappingCatalogue#hasMappingWithPartnerCode(PartnerCode)— Checks whether a mapping with the specifiedPartnerCodeexists in the mapping catalogue, to use to prevent deleting aPartnerCoursewith such aPartnerCode.
These operations are exposed in the SeplendidModel interface as SeplendidModel#addMapping(Mapping),
SeplendidModel#deleteMapping(Mapping), SeplendidModel#hasMapping(Mapping), SeplendidModel#hasMapping(LocalCode, UniversityName, PartnerCode),SeplendidModel#hasMappingWithLocalCode(LocalCode) and
SeplendidModel#hasMappingWithPartnerCode(PartnerCode) respectively.
When the user launches the application for the first time. All relevant data catalogues: LocalCourseCatalogue,
PartnerCourseCatalogue, UniversityCatalogue, MappingCatalogue are initialized with the initial state, containing
the seed data for that year's SEP.
Given below is an example usage scenario and how the addMapping mechanism works.
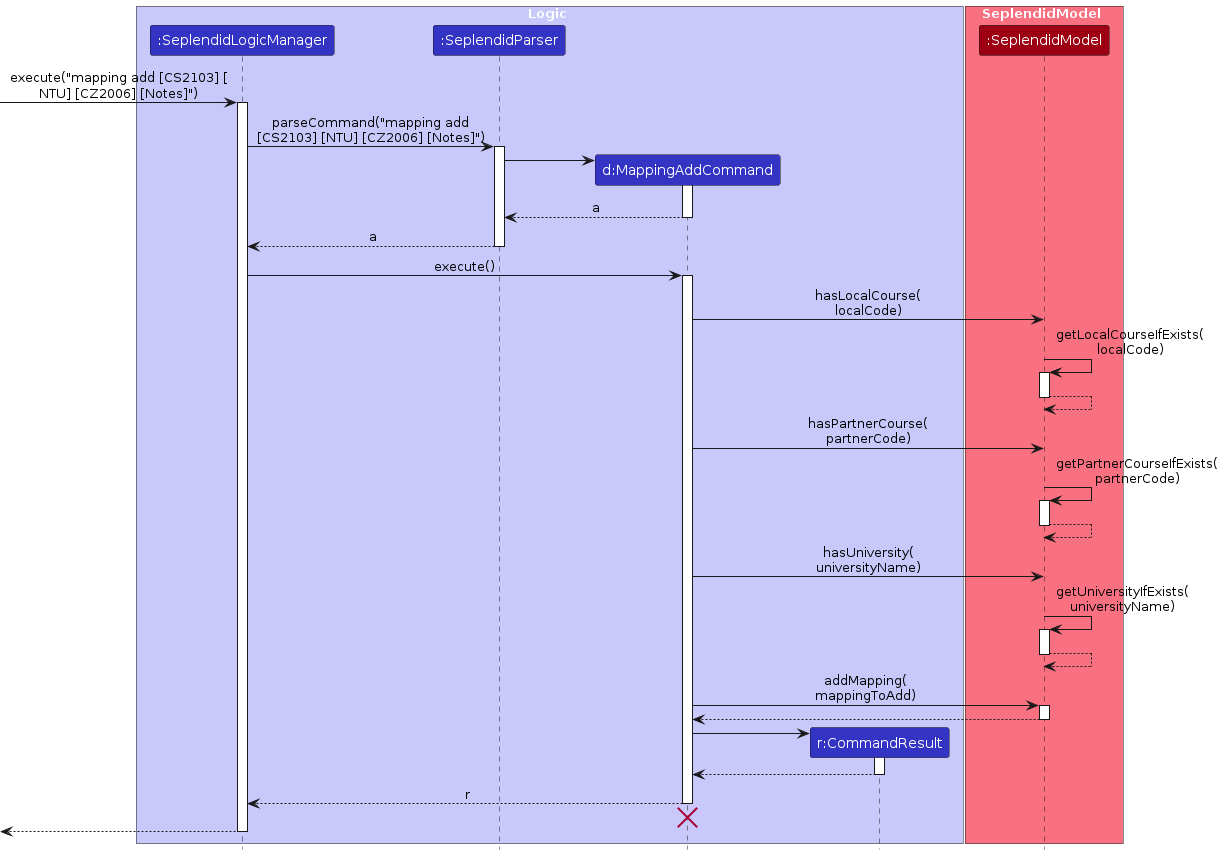
Before a mapping is added, the MappingAddCommand object will access the SeplendidModel instance to check if the
respective LocalCourse, PartnerCourse and University exists. If any of them does not exist, the command will
not execute SeplendidModel#addMapping.
Note: If a command fails its execution, no CommandResult will be returned, and hence no update to the UI or
storage files.
Note: The lifeline for MappingAddCommand should end at the destroy marker (X) but due to a limitation of
PlantUML, the lifeline reaches the end of diagram.
Similarly, the MappingDeleteCommand object will access the SeplendidModel instance to check if the mapping
exists, before deletion. Given below is an example usage scenario and how the deleteMapping mechanism works.
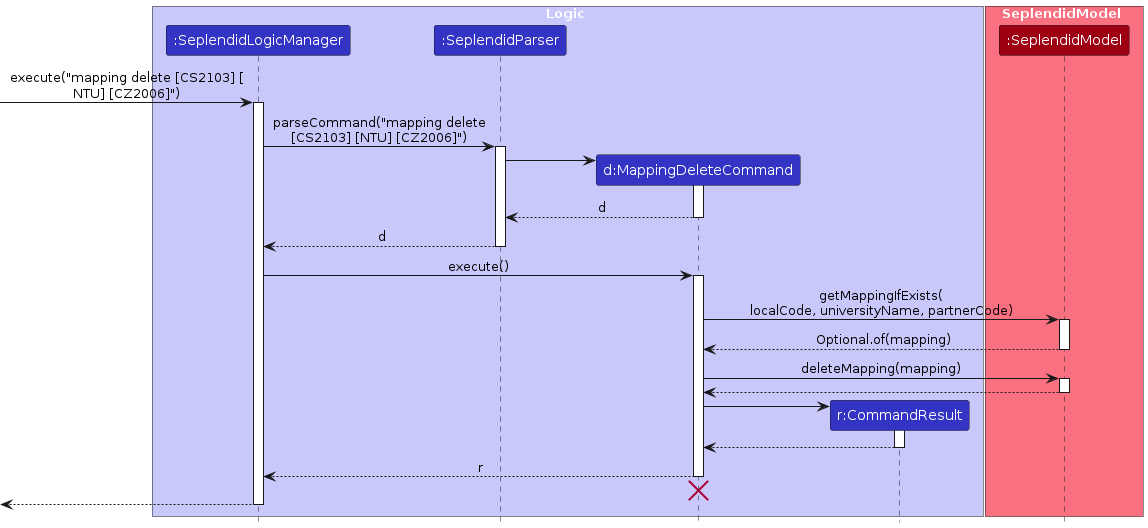
MappingDeleteCommand will call SeplendidModel#getMessageIfExists which returns an Optional<Mapping>. If it is
non-empty, the deletion will be performed, otherwise a CommandException will be thrown.
Design Considerations:
Aspect: How the dependency of Mapping on LocalCourse, PartnerCourse and University should be managed:
Alternative 1 (implemented choice): Disallow deletion of a
LocalCourseorPartnerCourseif it exists in a mapping.- Note that
Unviersityentries cannot be deleted as partner universities are fixed for every SEP application window. - Pros: Easy to implement, prevents accidental deletion.
- Cons: May have to delete a large number of mappings to remove a course (no force deletion feature).
- Note that
Alternative 2: Deleting a
LocalCourseorPartnerCoursewill delete all its associated mappings.- Pros: Will use fewer actions to delete a course, if there exists mappings it is tied to.
- Cons: We must ensure that deletion cascades, in order to maintain data integrity. This can introduce bugs if not done correctly.
6. Other Helpful Guides
7. Requirements
This section highlight the requirements that were considered when creating SEPlendid.
7.1 Product Scope
Target user profile:
This product is for NUS Computing students who are applying for Student Exchange Programme (SEP), who prefer a faster and more versatile tool to access SEP-related information, compared to the current EduRec system. Seniors who had underwent the exchange program, or students who learn about courses through their research can also contribute course mappings.
The following further describes our target users:
- has a need to view course mappings offered by partner universities
- is keen to contribute course mappings
- prefer desktop apps over other types
- can type fast
- prefers typing to mouse interactions
- is reasonably comfortable using CLI apps
Value proposition:
SEPlendid aims to provide an advanced search, allowing users to search for mappings by various attributes such
as partner universities' course names, and NUS course codes. We aim to also include features such as the ability to
contribute course mappings, and note-taking.
7.2 User Stories
Priorities: High (must have) - * * *, Medium (nice to have) - * *, Low (unlikely to have) - *
| Priority | As a … | I want to … | So that I can… |
|---|---|---|---|
* * * | student | view the list of local courses offered by NUS | plan my study guide to map my local courses for exchange |
* * * | student | view the list of partner courses offered by NUS' partner universities | plan my study guide to map to partner courses for exchange |
* * * | student | search a local course | find the local course I am interested to map |
* * * | student | search a partner course | find the partner course I am interested to map |
* * * | student | search a university | find the university I am interested to exchange in |
* * * | student | view the list of universities | see what universities I am interested in |
* * | student | sort the list of local courses by coursename or coursecode | easily review the local courses |
* * | student | sort the list of partner courses by coursename or coursecode | easily review the partner courses |
* * | student | sort the list of universities alphabetically | easily review the universities |
* * | student | delete a local course | remove local courses that can no longer be mapped |
* * | junior | delete a partner course | remove partner courses that can no longer be mapped |
* * * | student | view the list of mappings in SEPlendid | consider existing mappings for my exchange study plan |
* * * | student | add a mapping | to keep track of new mappings I discovered |
* * | student | delete a mapping | remove mappings that are obsolete |
* * | student | search for a mapping based on the code of the local/partner course | find the universities offering the course based on code |
* * | student | search for a mapping based on the name of the local/partner course | find the universities offering the course based on name |
* * | student | search for a mapping based on the name of a university | find the courses mappings offered by a partner university |
* | student | sort the list of mappings based on any attribute | easily review the mappings |
* * | student | update a local course | update the mapping list based on new information |
* * * | student | add notes | take note of the things I want to remember |
* * | student | view the list of my notes | easily view my notes that I have taken |
* * | student | delete my notes | remove my note |
* | student | update the list of my notes | edit any mistakes or update new information |
* | student | tag my notes | to organise my notes |
* | student | search for my notes based on the tag | to find my notes based on the tag |
* | student | clear the tags for my notes | to organise my notes based on tags |
7.3 Use Cases
For all use cases below, the System is the SEPlendid and the Actor is the user, unless specified otherwise
Local Course
Use case: List local course
MSS:
- User requests to list local courses.
- SEPlendid shows all available local courses. Use case ends.
Use case: Add a local course
MSS:
- User requests to add a local course.
- SEPlendid adds and shows the local course. Use case ends.
Extension:
1a. The command format is invalid.
- 1a1. SEPlendid shows an error message.
Use case resumes at step 1.
1b. The local course is already added.
- 1b1. SEPlendid shows an error message.
Use case resumes at step 1.
Use case: Delete a local course
MSS:
- User requests to delete a local course.
- SEPlendid deletes and shows the local course deleted.
Use case ends.
Extension:
1a. The command format is invalid.
- 1a1. SEPlendid shows an error message.
Use case resumes at step 1.
1b. The local course does not exist.
- 1b1. SEPlendid shows an error message.
Use case resumes at step 1.
Use case: Sorts local course
MSS:
- User requests to sort the list of local courses.
- SEPlendid sorts and shows sorted list of all available local courses.
Use case ends.
Extension:
1a. The command format is invalid.
- 1a1. SEPlendid shows an error message.
Use case resumes at step 1.
Partner course
Use case: List partner course
MSS:
- User requests to list partner courses.
- SEPlendid shows all available partner courses. Use case ends.
Use case: Add a partner course
MSS:
- User requests to add a partner course.
- SEPlendid adds and shows the partner course. Use case ends.
Extension:
1a. The command format is invalid.
- 1a1. SEPlendid shows an error message.
Use case resumes at step 1.
1b. The partner course is already added.
- 1b1. SEPlendid shows an error message.
Use case resumes at step 1.
Use case: Delete a partner course
MSS:
- User requests to delete a partner course.
- SEPlendid deletes and shows the partner course deleted.
Use case ends.
Use case: Sorts partner course
MSS:
- User requests to sort the list of partner courses.
- SEPlendid sorts and shows sorted list of all available partner courses.
Use case ends.
Extension:
1a. The command format is invalid.
- 1a1. SEPlendid shows an error message.
Use case resumes at step 1.
Extension:
1a. The command format is invalid.
- 1a1. SEPlendid shows an error message.
Use case resumes at step 1.
1b. The partner course does not exist.
- 1b1. SEPlendid shows an error message.
Use case resumes at step 1.
Use case: Sorts partner course
MSS:
- User requests to sort the list of partner courses.
- SEPlendid sorts and shows sorted list of all available partner courses.
Use case ends.
Extension:
1a. The command format is invalid.
- 1a1. SEPlendid shows an error message.
Use case resumes at step 1.
Mapping
Use case: List mappings
MSS:
- User requests to list available mappings.
- SEPlendid shows all available mappings. Use case ends.
Extension:
- 1a. Afterwards, the user can choose to bring up a detail panel of a mapping.
- 1a1. User clicks on a mapping item in the list.
- 1a2. SEPlendid shows the corresponding detail panel of the clicked-on mapping. Use case ends.
Use case: Add mappings
MSS:
- User requests to add a mapping.
- SEPlendid adds and show the mappings.
Use case ends.
Extension:
1a. The command format is invalid.
- 1a1. SEPlendid shows an error message. Use case resumes at step 1.
1b. The mapping is already added.
- 1b1. SEPlendid shows an error message. Use case resumes at step 1.
1c. A local course or partner course specified by user for the mapping does not exist.
- 1c1. SEPlendid informs the user through an error message that the course does not exist. Use case ends resumes at step 1.
Use case: Delete mappings
MSS:
- User requests to delete a mapping.
- SEPlendid deletes and shows the mappings deleted. Use case ends.
Extension:
1a. The command format is invalid.
- 1a1. SEPlendid shows an error message.
Use case resumes at step 1.
1b. The mappings does not exist.
- 1b1. SEPlendid shows an error message.
Use case resumes at step 1.
Use case: Sort mappings
MSS:
- User requests to sort the list of mappings based on an attribute.
- SEPlendid sorts and shows sorted list of all available mappings, based on specified attribute.
Use case ends.
Extension:
1a. The mapping command format is invalid.
- 1a1. SEPlendid shows an error message, detailing the mapping command set.
Use case resumes at step 1.
- 1a1. SEPlendid shows an error message, detailing the mapping command set.
1b. The mapping attribute specified is invalid.
- 1b1. SEPlendid shows an error message, detailing what attributes are available for sorting.
Use case resumes at step 1.
- 1b1. SEPlendid shows an error message, detailing what attributes are available for sorting.
2a. Afterwards, the user can choose to bring up a detail panel of a mapping.
- 2a1. User clicks on a mapping item in the list.
- 2a2. SEPlendid shows the corresponding detail panel of the clicked-on mapping.
Use case ends.
Use case: Search mappings
MSS:
- User requests to search the list of mappings based on an attribute, and given query.
- SEPlendid searches and shows sorted list of all available mappings, each which has a value for the specified
attribute that contains the query.
Use case ends.
Extension:
1a. The mapping command format is invalid.
- 1a1. SEPlendid shows an error message, detailing the mapping command set.
Use case resumes at step 1.
- 1a1. SEPlendid shows an error message, detailing the mapping command set.
1b. The mapping attribute specified is invalid.
- 1b1. SEPlendid shows an error message, detailing what attributes are available for sorting.
Use case resumes at step 1.
- 1b1. SEPlendid shows an error message, detailing what attributes are available for sorting.
1c. The query is empty.
- 1c1. SEPlendid shows an error message, detailing that the mapping command format.
Use case resumes at step 1.
- 1c1. SEPlendid shows an error message, detailing that the mapping command format.
2a. Afterwards, the user can choose to bring up a detail panel of a mapping.
- 2a1. User clicks on a mapping item in the list.
- 2a2. SEPlendid shows the corresponding detail panel of the clicked-on mapping.
Use case ends.
Universities
Use case: List universities
MSS:
- User requests to list the universities.
- SEPlendid shows all available universities.
Use case ends.
Use case: Search universities
MSS:
- User requests to search for a university.
- SEPlendid shows the specified university.
Use case ends.
Use case: Sort universities
MSS:
- User requests to sort the list of universities.
- SEPlendid shows the universities sorted alphabetically.
Use case ends.
Note
Use case: Add a note
MSS:
- User requests to add a note.
- SEPlendid adds and shows the note.
Use case ends.
Extension:
1a. The command format is invalid.
- 1a1. SEPlendid shows an error message.
Use case resumes at step 1.
Use case: List notes
MSS:
- User requests to list notes.
- SEPlendid shows all available notes.
Use case ends.
Use case: Update a note
MSS:
- User requests to list notes.
- SEPlendid shows all available notes.
- User requests to update a specific note in the list
- SEPlendid updates and shows the note.
Use case ends.
Extension:
2a. The list is empty. Use case ends.
3a. The command format is invalid.
3a1. SEPlendid shows an error message.
Use case resumes at step 2.
3b. The task does not exist.
- 3b1. SEPlendid shows an error message.
Use case resumes at step 2.
Use case: Delete a note
MSS:
- User requests to list notes.
- SEPlendid shows all available notes.
- User requests to delete a specific note in the list
- SEPlendid deletes the note.
Use case ends.
Extension:
- 2a. The list is empty.
Use case ends.
3a. The command format is invalid.
- 3a1. SEPlendid shows an error message.
Use case resumes at step 2.
3b. The task does not exist.
- 3b1. SEPlendid shows an error message.
Use case resumes at step 2.
Use case: Tag a note
MSS:
- User requests to list notes.
- SEPlendid shows all available notes.
- User requests to tag a specific note in the list
- SEPlendid tags and shows the note.
Use case ends.
Extension:
2a. The list is empty.
Use case ends.
3a. The command format is invalid.
- 3a1. SEPlendid shows an error message.
Use case resumes at step 2.
3b. The task does not exist.
- 3b1. SEPlendid shows an error message.
Use case resumes at step 2.
Use case: Search a note.
MSS:
- User requests to list notes.
- SEPlendid shows all available notes.
- User requests to filter notes based on tag.
- SEPlendid updates and shows the filtered notes.
Use case ends.
Extension: 2a. The list is empty. Use case ends.
3a. The command format is invalid.
3a1. SEPlendid shows an error message.
Use case resumes at step 2.
Use case: Clear tag a note.
MSS:
- User requests to list notes.
- SEPlendid shows all available notes.
- User requests to clear all tags a specific note in the list
- SEPlendid clears all the tags and shows the note.
Use case ends.
Extension:
2a. The list is empty.
Use case ends.
3a. The command format is invalid.
3a1. SEPlendid shows an error message. Use case resumes at step 2.
3b. The task does not exist.
3b1. SEPlendid shows an error message. Use case resumes at step 2.
7.4 Non-Functional Requirements
- Should work on any mainstream OS as long as it has Java
11or above installed. - Should be able to hold up to 1000 course mappings, along with its dependent data such as local courses, without a noticeable sluggishness in performance for typical usage.
- A user with above average typing speed for regular English text (i.e. not code, not system admin commands) should be able to accomplish most of the tasks faster using commands than using the mouse.
- The response to any use action should become visible within 5 seconds.
- The user interface should be intuitive enough for users who are not IT-savvy.
- The application should be designed to handle a growing database of course mappings and related data.
7.5 Glossary
- Mainstream OS: Windows, Linux, Unix, OS-X.
- Course Mapping: A course offered by a partner university, which NUS Computing students going on exchange can take, and is an equivalent course to one offered in NUS.
- CLI: Command-Line Interface is a means of interacting with a computer program b inputting lines of text called command-lines.
8. Instructions for Manual Testing
Given below are instructions to test the app manually.
Note: These instructions only provide a starting point for testers to work on; testers are expected to do more exploratory testing.
8.1 Launch and Shutdown
Initial launch
Download the jar file and copy into an empty folder
Double-click the jar file Expected: Shows the GUI with a set of sample courses. The window size may not be optimum.
Double-click the jar file
Expected: Shows the GUI with a set of sample local course. The window size may not be optimum.
8.2 Local Course
List all local courses
Prerequisite:
- There is at least 1 local course stored in SEPlendid.
localcourse list
Expected Output: All local courses stored in SEPlendid will be shown in the Item List Box.
Expected Output in the Command Output Box: Listed all local courses
Note: If there is no local course, the item list box will just be an empty box.
Add a local course
localcourse add [CS1111] [Test module] [4] [test]
Expected Output: The new local course will be added to the list of local courses.
Expected Output in the Command Output Box: New local course added message.
localcourse add [test]
Expected Output in the Command Output Box: Error for invalid command format.
Delete a local course
Prerequisite:
- A local course with local code of
CS1111currently exists in the local course list. - The local course specified should not be present in any of the current mappings.
localcourse delete [CS1111]
Expected Output: The local course will be deleted from the list of local courses.
Expected Output in the Command Output Box: Local course deleted message.
Update a local course
Prerequisites:
- A local course with local code of
BT1101currently exists in the local course list.
localcourse update [BT1101] [unit] [3]
Expected Output: The specified local course will be updated.
Expected Output in the Command Output Box: Local course updated message.
Search a local course by attributes
Prerequisite:
- There is at least 1 local course that have a localcode that contains the word
csstored in SEPlendid.
localcourse search [localcode] [cs]
Expected Output: A list of local courses that have a localcode of cs.
Expected Output in the Command Output Box: Local course searched message.
Prerequisite:
- There is no local course that have a localcode that contains the letter
zstored in SEPlendid.
localcourse search [localcode] [z]
Expected Output: No result.
Expected Output in the Command Output Box: Local course searched message.
Note: The query cannot start with a number. It must start with an alphabet.
Sort local courses by attributes
Prerequisite:
- There is at least 1 local course stored in SEPlendid.
localcourse sort [localname]
Expected Output: All local courses stored in SEPlendid will be shown in the Item List Box sorted according to the localname in ascending order.
Expected Output in the Command Output Box: Sorted all local courses
Note: If there is no local course, the item list box will just be an empty box.
8.3 Partner Course
List all partner courses
Prerequisite:
- There is at least 1 partner course stored in SEPlendid.
partnercourse list
Expected Output: All partner courses stored in SEPlendid will be shown in the Item List Box.
Expected Output in the Command Output Box: Listed all partner courses
Note: If there is no partner course, the item list box will just be an empty box.
Add a partner course
Prerequisite:
- The university of the partner course should be added to the university list.
partnercourse add [The Hong Kong Polytechnic University] [CS1111] [Test module] [4] [test]
Expected Output: The new partner course will be added to the list of partner courses.
Expected Output in the Command Output Box: New partner course added message.
partnercourse add [University of] [test]
Expected Output in the Command Output Box: Error for invalid command format.
Delete a partner course
Prerequisite:
- A partner course with partner code of
CS1111and university ofThe Hong Kong Polytechnic Universitycurrently exists in the partner course list. - The partner course specified should not be present in any of the current mappings.
partnercourse delete [The Hong Kong Polytechnic University] [CS1111]
Expected Output: The partner course will be deleted from the list of partner courses.
Expected Output in the Command Output Box: Partner course deleted message.
Update a partner course
Prerequisites:
- A partner course with partner code of
CSE469and university ofArizona State Universitycurrently exists in the partner course list.
partnercourse update [Arizona State University] [CSE469] [unit] [1]
Expected Output: The specified partner course will be updated.
Expected Output in the Command Output Box: Partner course updated message.
Search a partner course by attributes
Prerequisite:
- There is at least 1 partner course that have a partnercode that contains the word
csstored in SEPlendid.
partnercourse search [partnercode] [cs]
Expected Output: A list of partner courses that have a partnercode of cs.
Expected Output in the Command Output Box: Partner course searched message.
Prerequisite:
- There is no partner course that have a partnercode that contains the letter
zzstored in SEPlendid.
partnercourse search [partnercode] [zz]
Expected Output: No result.
Expected Output in the Command Output Box: Partner course searched message.
- Prerequisites: List all mappings using the
mapping listcommand. Multiple mappings in the list.
- Ensure your scroll to the bottom. Note: The query cannot start with a number. It must start with an alphabet.
Sort partner courses by attributes
- Other incorrect delete commands to try:
mapping ad,mapping add [],...
Expected: An error message will appear. Prerequisite:
- There is at least 1 partner course stored in SEPlendid.
partnercourse sort [university]
- Dealing with missing/corrupted data files
- If any of the
.jsonfiles found under thedata/directory created is edited to have invalid data. SEPlendid will reset to the default data, which has been programmatically added. - Therefore, it is recommended to make a copy and keep a backup of existing data before making any changes to any of
the files under
data/*.json. - One corrupted file will lead to a full reset of the application. Expected Output: All partner courses stored in SEPlendid will be shown in the Item List Box sorted according to the university in ascending order.
- To simulate a missing/corrupted data file, delete the
data/directory.
- A new director will be created in its place, with the default seed data.
- To corrupt the data, open any of the
.jsonfiles underdata/and edit the data in it. For instance, you may change alocalCodeto the empty string"". Restart the application, and observe that the data has been reset. Expected Output in the Command Output Box: Sorted all partner courses
Note: If there is no partner course, the item list box will just be an empty box.
8.4 University
List all universities
Prerequisite:
- There is at least 1 university stored in SEPlendid.
university list
Expected Output: All universities stored in SEPlendid will be shown in the Item List Box.
Expected Output in the Command Output Box: Listed all universities
Note: If there is no university, the item list box will just be an empty box.
Search a university by attributes
Prerequisite:
- There is at least 1 university that have a name that contains the word
hong kongstored in SEPlendid.
university search [hong kong]
Expected Output: A list of universities that have a name that contains hong kong.
Expected Output in the Command Output Box: University searched message.
Prerequisite:
- There is no university that have a name that contains the word
hkstored in SEPlendid.
university search [hk]
Expected Output: No result.
Expected Output in the Command Output Box: University searched message.
Sort universities
Prerequisite:
- There is at least 1 university stored in SEPlendid.
university sort
Expected Output: All universities stored in SEPlendid will be shown in the Item List Box sorted according to the name in ascending order.
Expected Output in the Command Output Box: Sorted all universities
Note: If there is no university, the item list box will just be an empty box.
8.5 Mapping
List all mappings
Prerequisite:
- There is at least 1 mapping stored in SEPlendid.
mapping list
Expected Output: All mappings stored in SEPlendid will be shown in the Item List Box.
Expected Output in the Command Output Box: Listed all mappings
Note: If there is no mapping, the item list box will just be an empty box.
Add a mapping
Prerequisite:
- The university of the partner course should be added to the university list.
- The local course with local code specified should be added to the local course list.
- The partner course with partner code specified should be added to the partner course list.
mapping add [CS3230] [Arizona State University] [CSE469] [mapping]
Expected Output: The new mapping will be added to the list of mappings.
Expected Output in the Command Output Box: New mapping added message.
mapping add [University of] [test]
Expected Output in the Command Output Box: Error for invalid command format.
Delete a mapping
Prerequisite:
- A mapping with local code of
CS3244, partner code ofCSE494and university ofArizona State Universitycurrently exists in the mapping list.
mapping delete [CS3244] [Arizona State University] [CSE494]
Expected Output: The mapping will be deleted from the list of mappings.
Expected Output in the Command Output Box: Mapping deleted message.
Search a mapping by attributes
Prerequisite:
- There is at least 1 mapping that have a localcode that contains the word
cs3230stored in SEPlendid.
mapping search [localcode] [cs3230]
Expected Output: A list of mappings that have a localcode that contains the word cs3230.
Expected Output in the Command Output Box: Mapping searched message.
Prerequisite:
- There is no mapping that have a localcode that contains the word
zstored in SEPlendid.
mapping search [localcode] [z]
Expected Output: No result.
Expected Output in the Command Output Box: Mapping searched message.
Sort mappings by attributes
Prerequisite:
- There is at least 1 mapping stored in SEPlendid.
mapping sort [localcode]
Expected Output: All mappings stored in SEPlendid will be shown in the Item List Box sorted according to the localcode in ascending order.
Expected Output in the Command Output Box: Sorted all mappings
Note: If there is no mapping, the item list box will just be an empty box.
8.6 Note
List all notes
Prerequisite: There is at least 1 note stored in SEPlendid.
note list
Expected Output: All notes stored in SEPlendid will be shown in the Item List Box.
Expected Output in the Command Output Box: Listed all notes
Note: If there is no note, the item list box will just be an empty box.
Add a note
note add [This is the content of the note] [tag]
Expected Output: The new note will be added to the list of notes.
Expected Output in the Command Output Box: New note added message.
note add [This note cannot be added] [test_]
Expected Output in the Command Output Box: Error for invalid command format.
Note: Note tag should consist of only alphanumeric characters and should not contain any whitespaces.
Delete a note
Prerequisite:
- A note with index 1 currently exists in the note list.
note delete [1]
Expected Output: The note will be deleted from the list of notes.
Expected Output in the Command Output Box: Note deleted message.
Update a note
Prerequisite:
- A note with index 1 currently exists in the note list.
note update [1] [The new content]
Expected Output: The specified note will be updated.
Expected Output in the Command Output Box: Note updated message.
Tag a note
Prerequisite:
- A note with index 1 currently exists in the note list.
note tag [1] [newtag]
Expected Output: The specified note will be updated.
Expected Output in the Command Output Box: Note tagged message.
Note: Note tag should consist of only alphanumeric characters and should not contain any whitespaces.
Clear tag a note
Prerequisite:
- A note with index 1 currently exists in the note list.
note cleartag [1]
Expected Output: The specified note will be updated.
Expected Output in the Command Output Box: Note cleartag message.
Search a note by tag
Prerequisite:
- There is at least 1 note that have a tag that contains the word
tagstored in SEPlendid.
note search [tag]
Expected Output: A list of notes that have a tag that contains tag.
Expected Output in the Command Output Box: Note searched message.
Prerequisite:
- There is no note that have a tag that contains the word
teststored in SEPlendid.
note search [test]
Expected Output: No result.
Expected Output in the Command Output Box: Note searched message.
Note: The query should consist of only alphanumeric characters and should not contain any whitespaces.
8.7 Saving Data
- Dealing with missing/corrupted data files
- If any of the
.jsonfiles found under thedata/directory created is edited to have invalid data. SEPlendid will reset to the default data, which has been programmatically added. - Therefore, it is recommended to make a copy and keep a backup of existing data before making any changes to any of
the files under
data/*.json. - One corrupted file will lead to a full reset of the application.
- To simulate a missing/corrupted data file, delete the
data/directory.
- A new director will be created in its place, with the default seed data.
- To corrupt the data, open any of the
.jsonfiles underdata/and edit the data in it. For instance, you may change alocalCodeto the empty string"". Restart the application, and observe that the data has been reset.
9. Planned enhancements
This section describes the planned enhancements for SEPlendid.
- Add the ability to allow update of mappings, to complement the existing mapping feature. This was not prioritised due to time constraints.
- Add memory for resizing of windows. The application should remember the window size from the latest run.
10. Effort
The implementation of SEPlendid proved to be a challenging endeavor. Below is the highlights of the extensive effort our team dedicated to developing SEPlendid, along with a mention of some of the challenges we encountered along the way.
10.1 Morphing of AB3 to SEPlendid
As mappings was the core feature of SEPlendid, we decided to morph AB3 into SEPlendid. We identified the need for
several data types, minimally LocalCourse, PartnerCourse, University and Mapping. We also identified the
unique identifiers for each data type, and the relationships between them. For instance, a Mapping object has a
LocalCode, PartnerCode and UniversityName object. LocalCode is the unique identifier (or in database terms,
the primary key) of LocalCourse, and {PartnerCode, UniversityName} is the unique identifier of PartnerCourse.
As the Mapping object is dependent on LocalCourse, PartnerCourse and University, we decided to decouple
these data storages, to avoid data redundancy and inconsistency. Initially, AB3 only offered 1 data storage, which
is the address book and this led us to refactor a large portion of the codebase to accommodate the new data types.
A new parser implementation was also required to handle the new command format.
One challenge we encountered was the need to access model for other data, such as LocalName of LocalCourse,
which is not part of the unique identifier, for the purpose of searching and sorting. Mapping did not consist of a
LocalName object, as it would lead to data redundancy. This challenge was solved with passing only the method
reference of a model method getLocalCourseIfExists to the comparators and predicates used. This follows for
partner courses.
A large portion of code had to be refactored to morph AB3 to SEPlendid.
10.2 Redesigning the UI
In recognising the significance of minimalism for achieving simplicity, we embarked on the task of redesigning the original AB3 UI into our custom SEPlendid interface. The endeavor underscored the essential balance between simplicity and functionality. The effort invested in the redesigning process was substantial, requiring meticulous design considerations. Striving to meet both aesthetic standards and high functionality, we faced a steep learning curve with JavaFX. Despite the initial challenges, our team persevered, overcoming obstacles and ultimately producing a UI that not only met our design goals but also offered a visually appealing and highly functional experience tailored to the requirements of a student exchange program mapping tool.